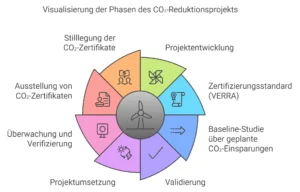
The organization Verra is under criticism like many certification programs for carbon offsets. Critics argue that the concept of CO₂ offsetting can be problematic in general because it allows companies to “buy their way out” by purchasing certificates, rather than actually reducing their emissions. Here are some of the main criticisms related to Verra and similar programs:
1. Effectiveness of Compensation Projects
A frequently criticized point is the actual effectiveness of the projects certified by Verra. Studies and reports suggest that some projects do not fully achieve the promised CO₂ savings. Especially with reforestation and forest protection projects (REDD+ projects), which are often certified under the Verra Verified Carbon Standard (VCS), it is questioned whether they can bind as much CO₂ in the long term as claimed. Forests are vulnerable to fires, deforestation, or other disturbances, which raises doubts about the permanence of carbon sequestration.
2. Additionality
The concept of “additionality” requires that only projects that would not have been implemented without the support of carbon certificates should be certified. Critics argue that some Verra-certified projects might have occurred even without the financial support from certificates, which reduces their actual emissions reduction impact. If projects would have taken place anyway, they do not make an additional contribution to climate protection and should not be counted as compensation.
3. Unclear Standards and Transparency
Although Verra sets certain standards and certifications, such as the Verified Carbon Standard (VCS), it is criticized that the processes for certifying and verifying the projects are not always transparent enough. Critics want more insights into the exact calculations, assumptions, and validations in order to better assess the effectiveness of the projects. Inadequate verification could lead to projects being falsely certified as climate-effective.
4. Moral Hazard and Greenwashing
CO₂ offsets, such as those offered by Verra, can tempt companies to focus on “greenwashing” rather than actively reducing their actual emissions. Critics argue that companies feel less pressure to make truly sustainable changes in their production and supply chains because of the simple possibility of offsetting. This could undermine the urgency to reduce emissions in the long term.
5. Inequalities and Social Impacts
Some Verra-certified projects, particularly forest protection projects, take place in developing countries and can affect local communities. Critics point out that such projects are sometimes carried out without sufficient involvement of the local population. In some cases, communities have no control over how their land use is restricted and do not always benefit sufficiently from the funds flowing into these projects.
Conclusion
Verra plays an important role in the voluntary carbon market, and despite the criticisms, many of its projects fulfill important environmental goals. However, the criticism shows that improvements in transparency, project monitoring, and the inclusion of local communities are necessary to ensure the credibility and actual climate impact of such programs. Further discussions and independent reviews could help address these challenges and strengthen the contribution of carbon offset projects to global climate protection.
More about the criticism of carbon offset programs can be found in the article on CO₂ offsetting on Wikipedia.