CO2 certificates are tradable permits that allow companies to emit a certain amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) or other greenhouse gases. These certificates are part of emission trading systems designed to reduce overall greenhouse gas emissions. Each certificate typically corresponds to one ton of CO2 that a company is allowed to emit.
The underlying idea behind these certificates is to create a financial incentive to reduce emissions. If a company lowers its emissions below the allowed amount, it can sell surplus certificates, providing an additional source of income. The introduction of CO2 certificates is a response to the growing concern about climate change and the need to reduce global emissions.
By creating a market for CO2 certificates, a price is set for emitting CO2, which encourages companies to invest in more environmentally friendly technologies and practices. This way, an economic incentive is created that benefits not only companies but also the environment. The idea is that by limiting the total number of available certificates, the pressure on companies to reduce their emissions and adopt more sustainable practices increases.
Key Takeaways
- CO2 certificates are tradable rights that allow companies to emit a certain amount of CO2.
- CO2 certificates are traded on special exchanges, where supply and demand determine the price.
- Companies that emit a lot of CO2 must buy CO2 certificates to offset their emissions.
- The trading of CO2 certificates operates through a limited number of certificates, which is reduced each year to decrease emissions.
- The benefits of CO2 certificates lie in creating incentives for companies to reduce emissions and invest in more environmentally friendly technologies.
How are CO2 certificates traded?
Flexibility through international trade
This trade can occur at both national and international levels, allowing companies to flexibly respond to their emission requirements. The price of CO2 certificates is determined by supply and demand.
Price fluctuations as an incentive
If many companies reduce their emissions and want to sell certificates, the price may drop. Conversely, an increase in demand for certificates can drive the price up. These price fluctuations can encourage companies to strategically plan their emissions and possibly invest in technologies that reduce emissions in the long term.
A dynamic process with economic and ecological considerations
The trading of CO2 certificates is thus a dynamic process that combines both economic and ecological considerations.
Which companies must buy CO2 certificates?
Typically, large industrial companies and energy providers are required to buy CO2 certificates. These companies are often the largest emitters of greenhouse gases and are therefore subject to strict legal requirements. Examples include power plants burning fossil fuels and production facilities in energy-intensive industries such as steel or cement manufacturing.
These companies must ensure they have enough certificates to cover their emissions; otherwise, they face significant fines. However, smaller companies and organizations may also need to acquire CO2 certificates in certain cases. Many countries have different regulations and thresholds at which companies are included in the emissions trading system.
This means that companies in less emissions-intensive sectors can also be affected under certain circumstances. The obligation to purchase CO2 certificates is therefore not limited to large companies; smaller players can also be involved in the trade.
How does the trading of CO2 certificates work?
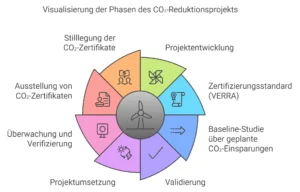
The trading of CO2 certificates occurs within a regulated framework, ensuring that all transactions are transparent and traceable. Initially, companies receive a certain number of certificates for free or must purchase them through auctions. This allocation is often based on historical emissions data or set benchmarks.
After the allocation, companies can trade their certificates on the market, either buying or selling depending on their individual situation. The trading platforms play a crucial role in the process of CO2 certificate trading. They provide the infrastructure for the exchange of certificates and ensure that all transactions comply with legal requirements.
Furthermore, there are mechanisms for monitoring and reporting companies’ emissions to ensure they meet their obligations. The entire process is designed to create a fair and efficient market for CO2 certificates while also providing incentives for companies to reduce their emissions.
What are the benefits of CO2 certificates?
The introduction of CO2 certificates offers numerous benefits for both companies and the environment. A key benefit is the economic incentive to reduce emissions. Companies have the opportunity to improve their environmental performance and achieve financial benefits through investments in sustainable technologies and processes.
Selling surplus certificates can provide an additional revenue source, thereby enhancing the competitiveness of the company. Another advantage is the flexibility the system offers. Companies can decide how to reduce their emissions – whether through technological innovations or by purchasing certificates on the market.
This flexibility allows companies to find tailored solutions that meet their specific needs. Moreover, the system raises awareness about climate change and promotes sustainable corporate governance.
How is the value of CO2 certificates determined?
The value of CO2 certificates is influenced by various factors, including supply and demand in the market as well as political frameworks. If many companies reduce their emissions and want to sell certificates, this may lead to an oversupply and drive the price down. Conversely, high demand for certificates can increase the price.
External factors such as international climate agreements or changes in legislation can also significantly affect the value of CO2 certificates. Additionally, economic conditions play a role in determining the price of CO2 certificates. In times of economic growth, energy demand may increase, leading to higher emissions and a greater need for certificates.
Conversely, economic crises may cause companies to reduce their production, requiring fewer certificates. This dynamic makes the CO2 certificate market complex and requires companies to continuously adjust their strategies.
What role do CO2 certificates play in the fight against climate change?
CO2 certificates play a central role in the global fight against climate change. They are a tool for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable practices in industry. By creating a financial incentive to reduce emissions, they help companies develop and implement more environmentally friendly technologies.
This is especially important given the alarming scientific findings about climate change and its impacts on our planet. Additionally, CO2 certificates enable international cooperation in climate protection. Countries can set their emission targets and mutually benefit through the trading of certificates.
This creates a global market for emission rights and fosters the exchange of technologies and best practices between countries. In this way, CO2 certificates not only help reduce emissions but also raise awareness of global environmental issues and promote sustainable development worldwide.
How can companies use CO2 certificates to operate more sustainably?
Companies can strategically use CO2 certificates to achieve their sustainability goals while also gaining economic benefits. By investing in technologies that reduce their emissions, they can not only lower their costs but also minimize their ecological footprint. Selling surplus certificates can also provide an additional revenue source, thereby increasing the company’s financial stability.
Moreover, companies can contribute to global climate protection by purchasing CO2 certificates from emission reduction projects in developing countries. This not only enhances the company’s image as a responsible actor in climate protection but also has a positive impact on local communities worldwide. Through these actions, companies can not only achieve their own goals but also make a significant contribution to fighting climate change, thus shaping a more sustainable future.
If you want to learn more about how you can personally contribute to reducing greenhouse gases, you should check out the article Your CO2 Footprint. This article offers practical tips and methods for calculating and understanding your own CO2 footprint. It’s an important step in recognizing where you can start reducing your emissions and becoming more conscious of the resources of our planet.